1 研究方法
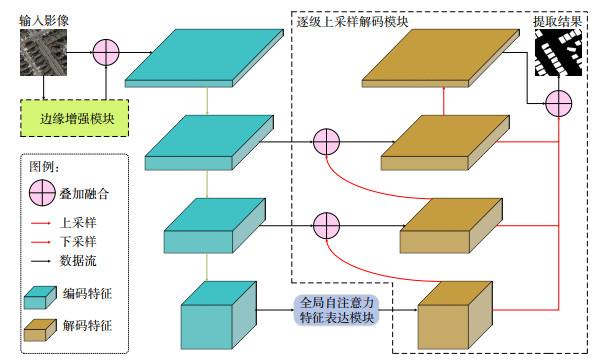
1.1 网络整体架构
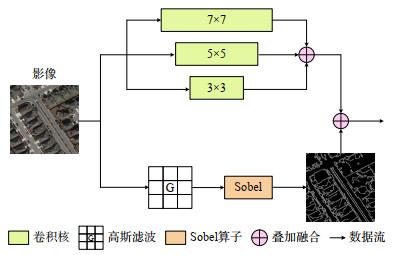
1.2 边缘增强模块
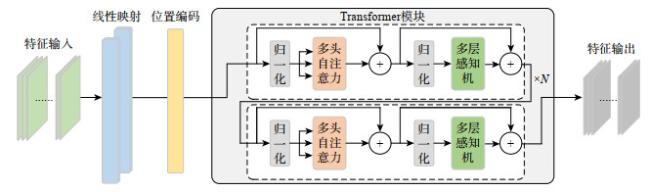
1.3 全局自注意力特征表达模块
1.4 逐级上采样解码模块
2 实验过程
2.1 数据集介绍
2.2 实验环境与训练细节
2.3 评价指标
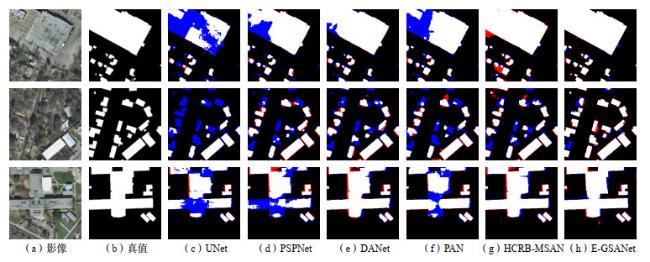
3 结果与分析
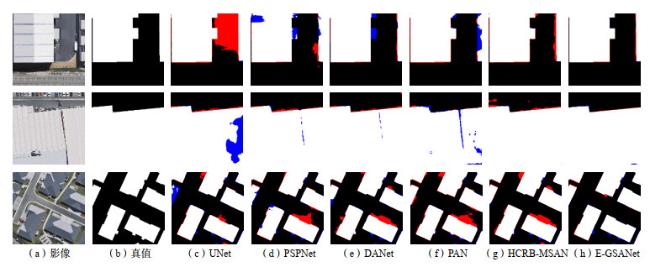
3.1 对比实验分析
表1 不同方法的对比结果 |
| 方法 | P/% | R/% | F1/% | IoU/% | OA/% |
| UNet* | 92.62 | 93.50 | 93.06 | 87.02 | 98.47 |
| PSPNet* | 93.41 | 91.95 | 92.68 | 86.35 | 98.40 |
| DANet* | 94.01 | 89.71 | 91.81 | 84.86 | 98.24 |
| PAN* | 92.80 | 91.49 | 92.14 | 85.43 | 98.28 |
| MA-FCN | 94.50 | 94.20 | 94.30 | 89.50 | — |
| SRI-Net | 95.21 | 93.28 | 94.23 | 89.09 | — |
| HCRB-MSAN | 96.78 | 94.68 | 95.72 | 91.79 | 99.07 |
| E-GSANet | 96.82 | 95.00 | 95.90 | 92.13 | 99.11 |
注:*表示没有提供精度结果的算法,使用官方或开源代码复现算法并得到了相应的测试结果。 |
表2 INRIA建筑物数据集上不同方法的对比结果 |
| 方法 | P/% | R/% | F1/% | IoU/% | OA/% |
| UNet* | 82.73 | 80.09 | 81.39 | 68.61 | 95.06 |
| PSPNet* | 81.63 | 86.55 | 84.02 | 72.45 | 95.56 |
| DANet* | 82.66 | 84.37 | 83.51 | 71.68 | 95.51 |
| PAN* | 90.11 | 77.02 | 83.05 | 71.02 | 95.76 |
| FPCRF | — | — | 87.65 | 74.79 | 95.81 |
| SRI-Net | 85.77 | 81.46 | 83.56 | 71.76 | — |
| HCRB-MSAN | 89.56 | 88.13 | 88.84 | 79.92 | 97.01 |
| E-GSANet | 88.26 | 89.87 | 89.06 | 80.28 | 97.02 |
注:*表示没有提供精度结果的算法,使用官方或开源代码复现算法并得到了相应的测试结果。 |
3.2 消融实验分析
表3 E−GSANet各模块的消融实验结果 |
| 边缘增强模块 | 全局自注意力特征表达模块 | 逐级上采样解码模块 | P/% | R/% | F1/% | IoU/% | OA/% |
| — | — | — | 91.43 | 93.09 | 92.25 | 85.62 | 98.28 |
| — | — | √ | 94.98 | 94.93 | 94.95 | 90.39 | 98.89 |
| — | √ | √ | 95.81 | 94.88 | 95.34 | 91.10 | 98.98 |
| √ | √ | √ | 96.82 | 95.00 | 95.90 | 92.13 | 99.11 |