1 钻探工作量
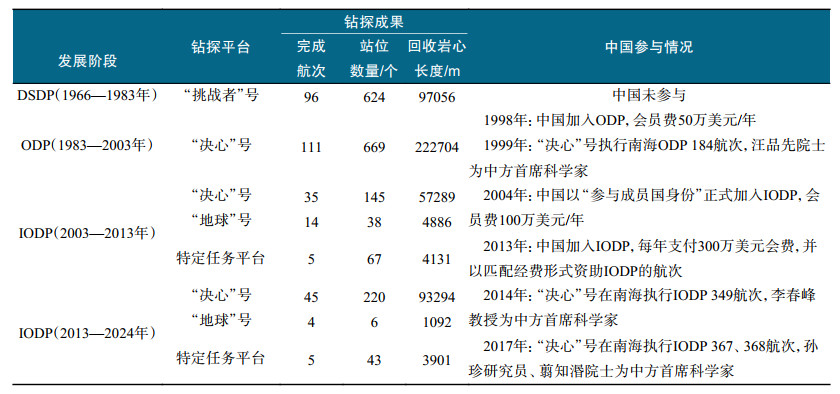
表1 国际大洋钻探计划各阶段钻探成果及中国参与情况 |
 |

国际大洋钻探的科学成就及未来展望
|
朱婵,工程师,研究方向为海洋发展战略与政策研究,电子信箱:zhuchan1992@qq.com |
收稿日期: 2024-11-21
网络出版日期: 2025-04-11
基金资助
国家自然科学基金青年科学基金项目(42306089)
广东省哲学社会科学规划2023年度重大项目(GD23ZD07)
版权
Major achievements of ocean scientific drilling and future perspective
Received date: 2024-11-21
Online published: 2025-04-11
Copyright
系统梳理国际大洋钻探50余年的钻探工作量、样品资料积累,以及在地球动力学、气候演变规律、生命起源与演化和海洋自然灾害等领域的重大科学成果产出,并分析了新形势下大洋钻探的在运营体系、数据资料管理与应用及科学目标制定等方面的发展方向。科学大洋钻探历经半个多世纪,不断刷新钻探的深度和广度,但全球洋底仍然存在大范围待探索的区域和亟待解决的科学问题。随着美国“决心”号钻探船退出历史舞台,欧洲、日本联合启动新一轮大洋钻探计划(IODP3),中国“梦想”号钻探船建成入列之际,IODP国际格局将迎来重大变革,中国科学家应当围绕国家战略发展需求,紧跟前沿科学领域,加强国际交流与合作,充分发挥自身优势,在未来科学大洋钻探领域占据主导权。
朱婵 , 陈红瑾 , 杨伦庆 , 韩冰 . 国际大洋钻探的科学成就及未来展望[J]. 科技导报, 2025 , 43(5) : 79 -88 . DOI: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2024.11.01630
表1 国际大洋钻探计划各阶段钻探成果及中国参与情况 |
 |
| 1 |
汪品先. 大洋钻探五十年: 回顾与前瞻[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63 (36): 3868- 3876.
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
王文涛, 王金平, 揭晓蒙, 等. 面向2024年后的中国引领的国际大洋钻探计划管理与运行机制思考[J]. 海洋科学, 2022, 46 (2): 127- 134.
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
汪品先, 翦知湣. 探索南海深部的回顾与展望[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2019, 49 (10): 1590- 1606.
|
| 7 |
Backman J, Moran K, McInroy D, et al. Expedition 302 summary[J/OL]. Geology, Environmental Science, 2006, doi: 10.2204/IODP.PROC.302.101.2006.
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
鲁铮博, 史宇坤, 华洪, 等. 国际大洋科学钻探的数据资源与共享现状[J]. 高校地质学报, 2020, 26 (4): 472- 480.
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
Mayer L, Theyer F, Barron J, et al. Initial reports of the deep sea drilling project[J/OL]. Geology, Environmental Science, 1985, doi: 10.2973/DSDP.PROC.85.1985.
|
| 13 |
Luyendyk B, Davies T. Results of DSDP leg 26 and the geologic history of the southern Indian ocean[EB/OL]. [2024-12-30]. http://deepseadrilling.org/26/volume/dsdp26_36.pdf.
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
Frey F, Coffin M, Wallace P, et al. Leg 183 synthesis: Kerguelen plateau-broken ridge-a large igneous province[C]//Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program. College Station, TX, USA: Texas A&M University Ocean Drilling Program, 2003: 1-48.
|
| 16 |
方家松, 李江燕, 张利. 海底CORK观测30年: 发展、应用与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 2017, 32 (12): 1297- 1306.
|
| 17 |
Becker K, Davis E E. A review of CORK designs and operations during the Ocean Drilling Program[C]//Proceedings of the IODP. IODP, 2005, doi: 10.2204/iodp.proc.301.104.2005.
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
翦知湣, 党皓文. 解读过去、预告未来: IODP气候与海洋变化钻探研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 2017, 32 (12): 1267- 1276.
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
田军. 新生代的气候节律: 赤道太平洋IODP320、321航次[J]. 地球科学进展, 2009, 24 (12): 1357- 1361.
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
拓守廷, 王文涛. 国际大洋钻探2050科学框架及其对未来大洋钻探发展的启示[J]. 地球科学进展, 2022, 37 (10): 1049- 1053.
|
| 34 |
冉皞, 张涛. 近十年大洋科学钻探进展与未来重点发展方向[J]. 中国地质, 2024, 51 (3): 1091- 1094.
|
| 35 |
徐晶晶, 张涛, 吴林强, 等. 大洋科学钻探特点与发展趋势: 基于国际大洋发现计划科学框架的对比分析[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2023, 40 (3): 30- 38.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |