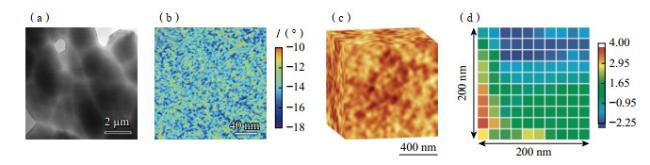
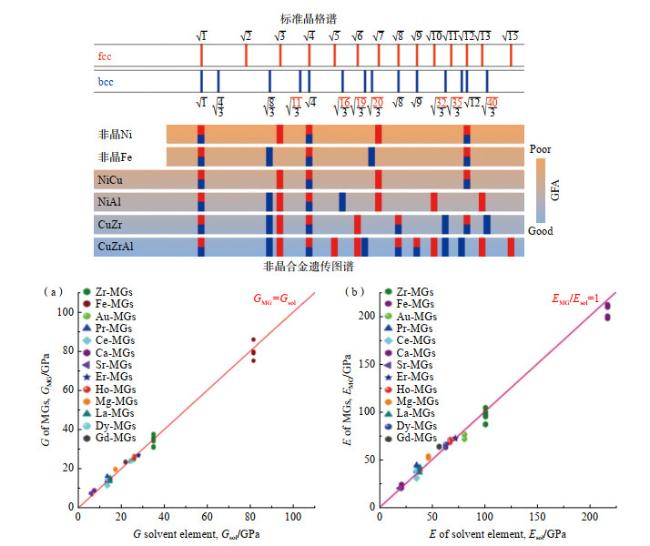
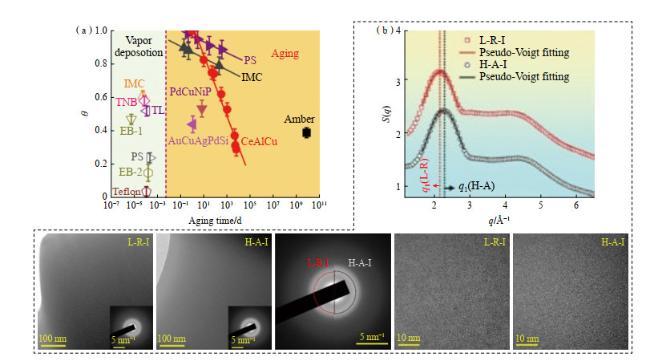
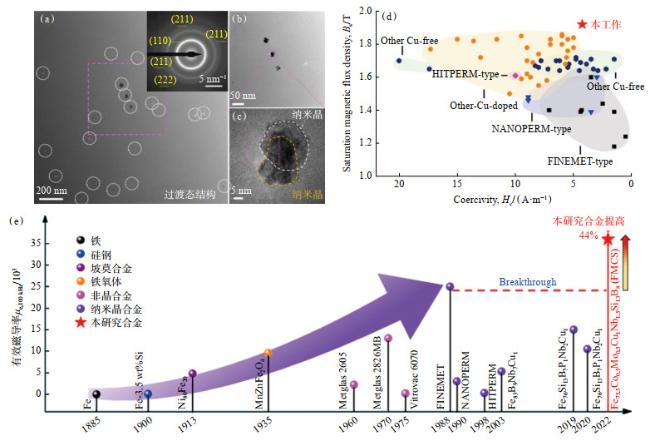
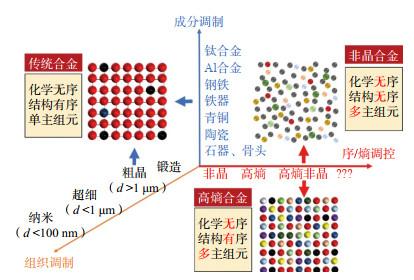
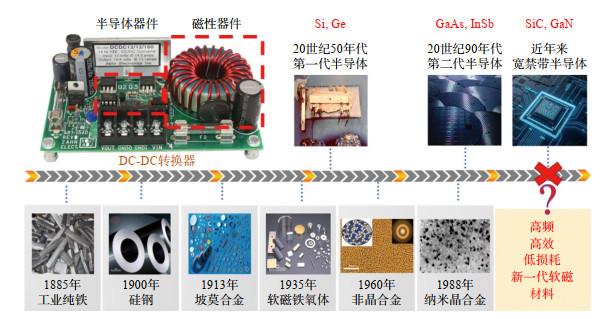
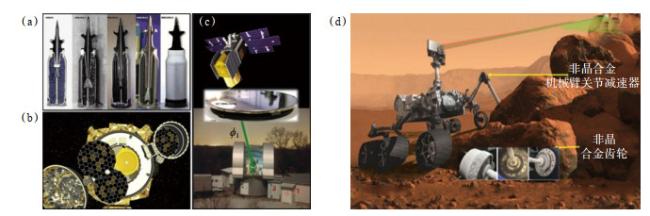
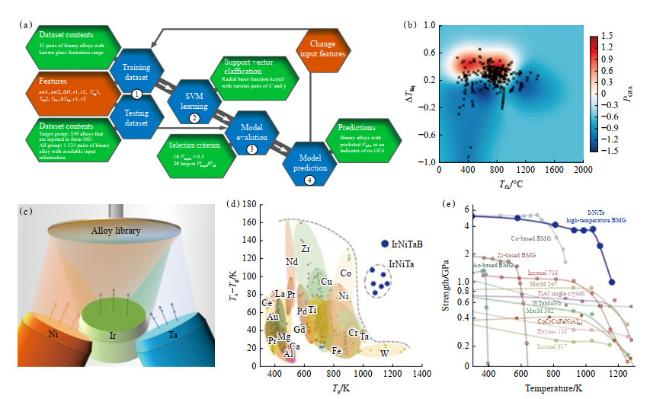
现代电子电力设备逐渐向小型化、高效化和节能化发展,这对软磁合金材料的软磁性能提出了更高的要求。非晶合金由于其独特的无序结构,表现出极其优异的软磁性能,如高磁导率、低矫顽力、低损耗等特点,广泛应用于各类电力电子的磁性器件中,具有显著的节能环保优势。2022年,松山湖材料实验室通过全新成分设计思路,成功开发出了一种结构介于传统非晶合金和纳米晶合金之间的新型软磁合金材料,表现出超高的磁感应强度
Bs(高达1.94 T)和低至4.3 A/m的低矫顽力
Hc,打破了铁基非晶纳米晶合金体系中
Bs和
Hc之间的互斥关系,可以应用在如高速电机、大功率光伏并网逆变器等现代电子产品中(
图 12(a−
d))
[23]。此外,对非晶合金进行合适的热处理,可在非晶基体上析出细小、均匀的纳米晶体,从而得到纳米晶软磁合金,该类材料同样具有意想不到的优异软磁性能。
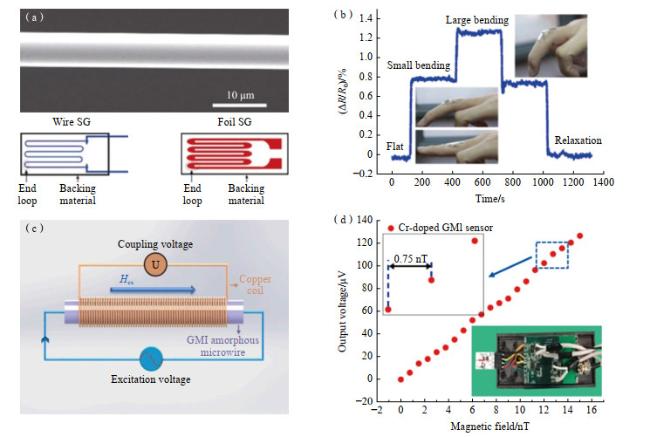
图 12(e)[24]是近期松山湖材料实验室和中国科学院物理所在非晶合金前驱体基础上开发出具有最高高频磁导率的新型软磁非晶纳米晶合金材料,在100 kHz下的有效磁导率高达36000(比目前磁导率最高的FeSiBCuNb纳米晶合金高44%),并且随着频率的提高,优势变得更加显著,同时表现出较高饱和磁感应强度(1.42 T)、低损耗(120 kW/m
3 @0.2 T,100 kHz)。该材料还具有较低的材料成本和良好的玻璃形成能力。对于实现高频电子器件以及高速电机的高效率、小体积和大功率的优势起着至关重要的作用。可以看到,Fe基等非晶合金/纳米晶材料拥有优异的软磁性能,被誉为新型绿色能源材料,在电机、变压器、电感等电工装备领域具有广阔的市场和应用前景。