1 研究设计与研究框架
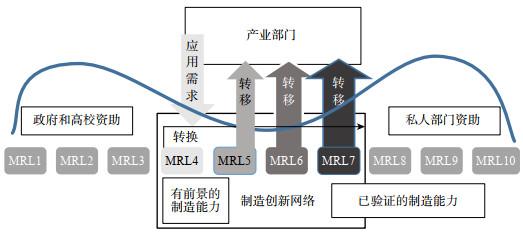
1.1 政府支持制造技术联盟的内在机制
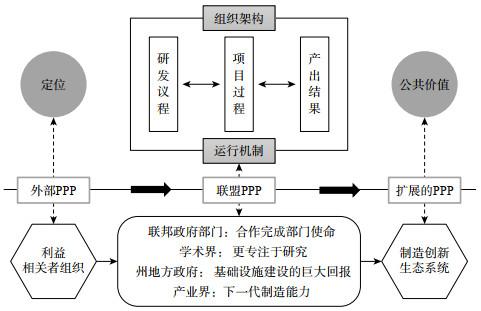
1.2 政府支持下制造技术联盟的公共价值创造分析框架
1.3 案例适用性
2 美国国家制造创新网络的公共价值创造机制分析
2.1 公共价值与使命
2.2 合法性与政治支持
2.3 行动能力塑造
3 美国国家制造创新网络公共价值实现结果
表1 2016—2021年美国国家制造创新网络绩效指标值 |
| 度量类别 | 具体指标 | 计量单位 | 2016年 | 2017年 | 2018年 | 2019年 | 2020年 | 2021年 |
| 对美国创新生态系统的影响 | 有创新所会员协定的伙伴组织数目 | 会员总数 | 830 | 1291 | 1937 | 1920 | 2013 | 2320 |
| 成员多样性 | 大型厂商数量(500人以上) | 187 | 295 | 371 | 369 | 355 | 407 | |
| 小型制造商数量(500人以下) | 361 | 549 | 858 | 805 | 895 | 1053 | ||
| 学术成员人数(大学、社区学院等) | 177 | 297 | 474 | 463 | 459 | 516 | ||
| 其他实体数目(政府成员,政府实验室、非营利组织等) | 105 | 150 | 244 | 283 | 304 | 344 | ||
| 财务杠杆 | 每个财政年度的共同投资总额 | 每个财政年度的费用分摊额和任何不属于基本联邦资金的联邦资金/百万美元 | 218.9 | 177.8 | 313.5 | 355 | 262 | 314 |
| 技术进展 | 积极研究及发展项目的数目及价值 | 每个财政年度正在进行的项目个数(每个财政年度已完成、启动和跨越的项目) | 191 | 273 | 476 | 561 | 534 | 708 |
| 本财政年度创新所支出总额/百万美元 | 333.8 | 298.5 | 496.9 | 488 | 425 | 481 | ||
| 每个财政年度关键项目技术目标的实现百分比 | 每个财政年度达到关键里程碑的百分比/% | 82 | 79 | 82 | 80 | 79 | 82 | |
| 发展先进的制造业劳动力 | STEM活动 | 参加学院实习项目或培训的学生人数 | 23560 | 185425 | 200169 | 32951 | 55478 | 67115 |
| 劳动力中完成证书、学徒或培训项目的人数 | 3386 | 4302 | 2630 | 6120 | 9284 | 14676 | ||
| 教育/培训师参与 | 参加学院主导培训的教师或培训人员人数 | 1023 | 1299 | 2455 | 805 | 5411 | 5610 |
注:来源于美国国家先进制造办公室给国会的报告(AMNPO,2016;2017;2018;2019;2021a;2021b;2022)。 |